Investing in a Delaware Statutory Trust using a 1030 exchange can be an excellent way to exchange a high-maintenance commercial or rental property for a low-maintenance passive investment for beneficial interest. This article aims to delve deeper into the DST 1031 exchange, how it works, and more. Let’s begin
A DST 1031 exchange is a partial or fractional ownership property investment structure that enables an unlimited number of investors to own real estate jointly. Due to how a DST operates, with a sponsor taking on the managerial and decision-making role, it is a no-maintenance or low-maintenance way to own property.
According to a 2004 IRS ruling, when you own a share of a DST 1031 exchange, you can seamlessly trade a business property or investment for the share, which results in deferring capital gains.
How Does a DST Work?
A Delaware Statutory Trust is akin to a Limited Liability Company because all dividends and income are passed and taxed on an individual level instead of on a group level. There are various advantages to the DST model; for one, it is much cheaper and simpler to create and operate one while enjoying the limited liability benefits associated with an LLC.
A DST is created by a sponsor, who in turn names trustees that oversee the trust’s assets daily. The DST 1031 exchange sponsor could be an organization or an individual. They are required to locate and purchase property on the DST’s behalf.
The trust is responsible for collating the investment capital, arranging financing, and hiring property managers for the purchased property. By design, the trust directly owns the properties and other assets, while investors own stocks of the trust.
A DST generally pays consistent dividends to investors monthly, showing that this form of investment isn’t simply about increasing the value of a property. The typical investment timeline for a DST is between 5 to 10 years.
How Does the DST 1031 Exchange Work?
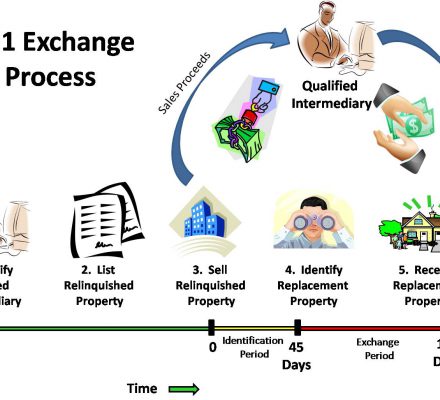
Considering that the IRS considers a DST stock a like kind property, the DST 1031 exchange functions in the same manner a traditional 1031 exchange does—albeit with a few differences.
Firstly, finding a DST to invest in can be difficult. It is not as simple as searching the local listings for an investment property. Real estate investors typically enlist the services of a securities broker-dealer to find a DST. The broker-dealer is responsible for presenting investors with numerous investment opportunities based on their risk appetite and other variables.
Secondly, while there are rules that must be adhered to in a 1031 exchange, purchasing a share in a DST 1031 exchange as a replacement property means you will want to leverage the 200% rule.
The 200% rule states that a DST investor can get up to 200% of the value of your exchanged property. This means you don’t have to follow the 3 property rule, which requires you to find a maximum of three substitutes for your replacement property.
This is because most DST 1031 exchanges comprise more than three properties. According to the 2004 IRS ruling, only passive real estate can qualify for the DST 1031 exchange.
Interested in joining a real estate investment club? Find out more here.
Types of DST 1031 Exchange Properties
DST properties typically fall into the categories below:
Office Space
Office space made up 6% of all DST 1031 exchange properties in 2020. You should note that office and retail real estate are seen as high risk; however, they have higher prospective yields.
Industrial
Industrial properties in 2020 made up almost 7% of DST 1031 exchange properties.
Self-Storage Facilities
Self-storage facilities are becoming an increasingly popular property type for DSTs, making up 7.3% of a typical DST 1031 exchange.
Residential
Statistics state that in 2020, multifamily units made up 51.2% of DST 1031 exchange properties. Residential investments are considered safe, as there will always be a demand; however, these real estate investment opportunities offer a lower yield than other property types.
How Much Leverage Can One Have in a DST 1031 Exchange?
The amount of leverage available in a DST 1031 exchange typically depends on the situation you are in. a requirement for the DST 1031 exchange is that you need to take on at least the same level of debt with the replacement property. The DST broker-dealer will provide choices that utilize different degrees of leverage. You must find one that meets the requirements of the 1031 exchange.
The great thing about a DST 1031 exchange is that it typically utilizes non-recourse financing, which means you don’t have to qualify for a loan since the property itself is the collateral. Non-recourse financing typically lasts 7 to 20 years and becomes locked in before the DST 1031 exchange property is taken to the market.
If you buy a DST leveraged property, you typically get a proportional percentage of the main down payment. This means you are creating equity in the building, yet another advantage of the DST 1031 exchange.
Fees Associated With A DST 1031 Exchange
Most people believe DSTs are much more costly than buying real estate directly. While DSTs have their own fees and commissions, directly purchasing real estate comes with uncapped and hidden fees that are much higher.
The fees associated with purchasing real estate directly are typically higher than DST fees since typical real estate purchases calculate expenses as a portion of debt and equity. In a way, the more valuable a property is, the higher the fees.
Conversely, DSTs do not use debt to determine fees, resulting in much lower fees. Additionally, DSTs closing costs are typically factored into the buy price. With that in mind, here are the fees you can expect to encounter in a DST 1031 exchange:
Selling Expenses and Costs
Expenses such as broker-dealer allowances and commissions for registered representatives can be 8 to 10% of equity.
Ongoing Property Management Fee
This fee is a percentage of property-generated income and can be based on performance. The fee is usually 3 to 4% of adjusted gross revenue.
Continuous Asset Management Fee
Since the DST 1031 exchange sponsor is responsible for the continuous management of the property, they are due payment for services such as attorneys, underwriters, lenders, communications, process distributions, bookkeeping, and more. The fee is usually 1 to 2% of the adjusted annual gross revenue.
Disposition Fee
This is the fee due when the property is sold. This fee is typically capped at 2 to 3% of the gross sale price.
Acquisition Fee
This fee is due to the broker-dealer or sponsor of the DST from the trust for identifying, vetting, and securing the property. It typically costs 2% of the buy price or 5 to 8% of equity.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of a DST 1031 Exchange
As with any investment, a DST 1031 exchange comes with some pros and some cons.
Advantages
No obligations to manage the property
By design, the DST 1031 exchange sponsor is the only person responsible for seeing to the asset management, bookkeeping, repairs, rent collection, and more.
Readily available
DST 1031 exchanges are readily available, especially for new buy-ins. This can be particularly useful for investors almost at their 45-day identification deadline or 180-closing day deadline. It is important to note that once a DST 1031 exchange buy-in period closes, it cannot be reopened.
Non-recourse financing
Most DDST 1031 exchanges utilize non-recourse financing, meaning that the property itself is the collateral for the loan. Participants in the DST don’t have to worry about getting personally-backed loans.
Access
The DST 1031 exchange is one of the best methods to access properties with a valuation between $25 million and $125 million. This includes grocery stores, apartment complexes, healthcare facilities, and other buildings occupied by AAA credit tenants.
Diversification
Instead of simply placing all your capital into a solitary replacement property as a real estate investor, a DST 1031 provides you with the opportunity to purchase portions of multiple properties. This can be particularly useful if you want to conduct a DST 1031 exchange of a single property for various replacements.
Low entry fee
Investing in a DST 1031 exchange can cost as little as $25000, a sum much less than most other realty-based investments.
Disadvantages
Inability to raise new capital
The 2004 IRS ruling also states that once the DST 1031 exchange buy-in period closes, it cannot be reopened or accept new contributions. This means it will have to be self-sufficient.
No control
Due to the ruling by the IRS in 2004, investors are required to relinquish the daily control of the trust to its trustees.
Illiquid
DST 1031 exchanges are generally long-term investments, which means they are held for a minimum of 5 years.
Selling a DST 1031 Exchange Property
Generally, when a 1031 exchange DST property is sold, all investors can create another one, further deferring their capital gain tax. Considering a DST is viewed as like kind property, it is possible to conduct a 1031 exchange into a new DST or transform it back into individual properties. This flexibility makes the DST 1031 exchange a great tax-deferral tool.